History
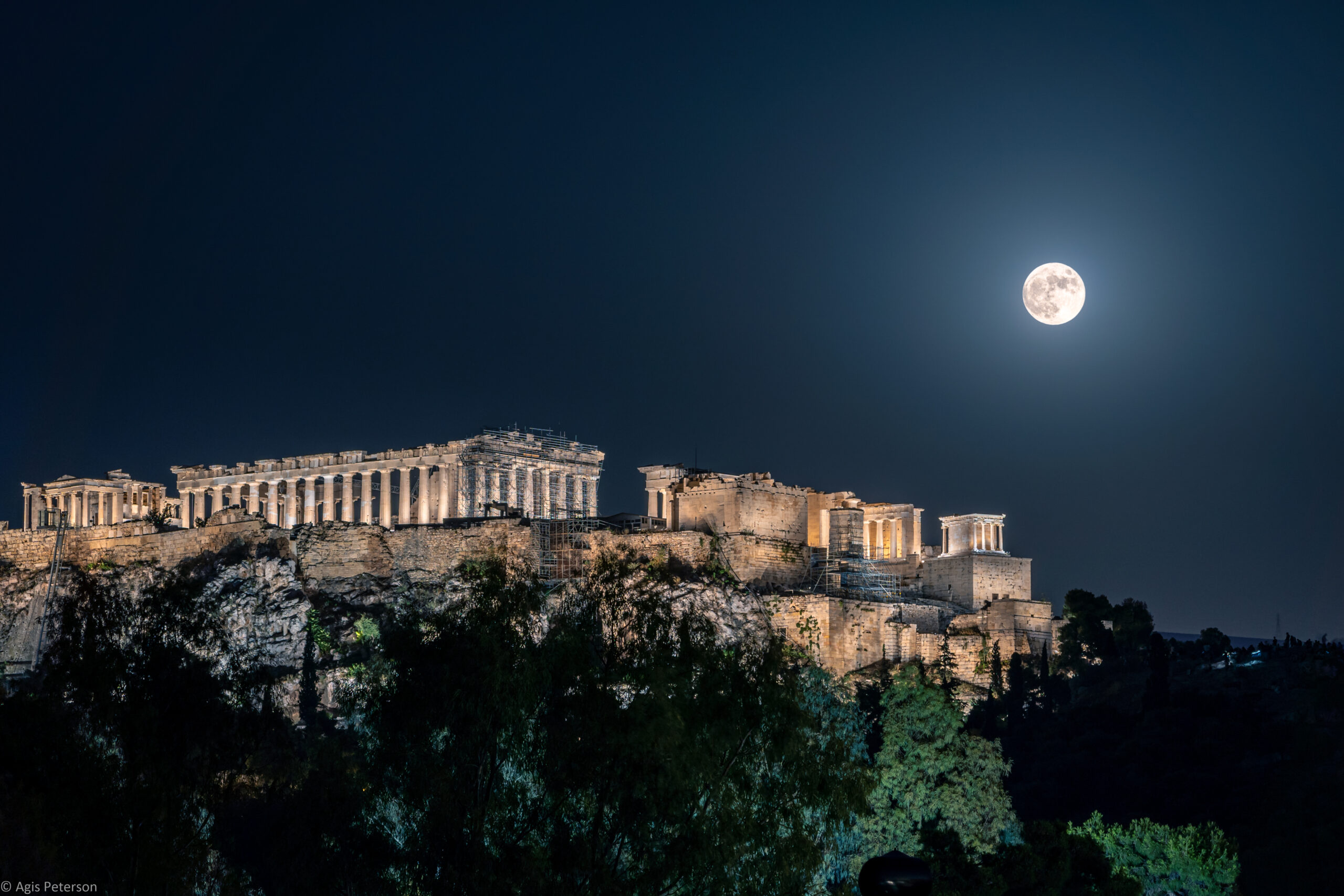
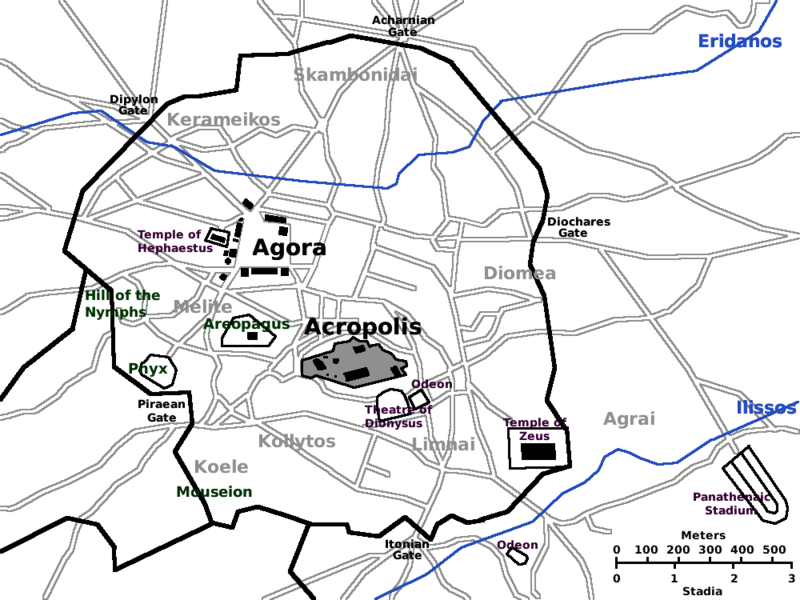
In the heart of ancient Athens
Theater of Dionysus
- Distance: 750m
- 10' walk (via Apostolou Pavlou st)
- Location on the map
- Directions from Acropolis Vision

The Theatre of Dionysus (or Theatre of Dionysos) is an ancient theatre in Athens on the south slope of the Akropolis hill, part of the sanctuary of Dionysos Eleuthereus (Dionysus the Liberator). The first orchestra terrace was constructed on the site around the mid-to late-6th century BC, where it hosted the City Dionysia.
Temple of Hephaestus
- Distance: 850m
- 10' walk (via Adrianou st)
- Location on the map
- Directions from Acropolis Vision

The Temple of Hephaestus or Hephaisteion (also "Hephesteum"; Ancient Greek: Ἡφαιστεῖον, or earlier as the Theseion (also "Theseum"; Ancient Greek: Θησεῖον), is a well-preserved Doric peripteral Greek temple; located on top of the Agoraios Kolonos hill.
Roman Agora
- Distance: 850m
- 11' walk (via Adrianou st)
- Location on the map
- Directions from Acropolis Vision

The Roman Agora (Greek: Ρωμαϊκή Αγορά) at Athens is located to the north of the Acropolis and to the east of the Ancient Agora.The Roman Agora has not today been fully excavated, but is known to have been a peristyle open space.
Parthenon
- Distance: 900m
- 12' walk (via Apostolou Pavlou st)
- Location on the map
- Directions from Acropolis Vision

The Parthenon (Ancient Greek: Παρθενών; Greek: Παρθενώνας, Parthenónas, [parθeˈnonas]) is a former temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, dedicated to the goddess Athena, whom the people of Athens considered their patron.
Odeon of Herodes Atticus
- Distance: 900m
- 12' walk (via Apostolou Pavlou st)
- Location on the map
- Directions from Acropolis Vision

The Odeon of Herodes Atticus (also called Herodeion or Herodion) is a stone Roman theater structure located on the southwest slope of the Acropolis of Athens, Greece. The building was completed in 161 AD and then renovated in 1950.
Areopagus Hill
- Distance: 1km
- 14' walk (via Apostolou Pavlou st)
- Location on the map
- Directions from Acropolis Vision
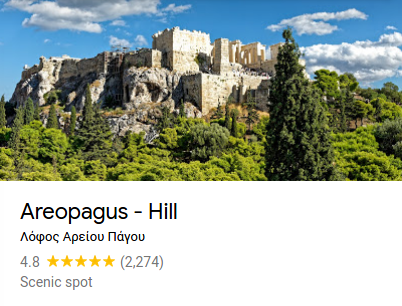
The Areopagus (/ˌæriˈɒpəɡəs/) is a prominent rock outcropping located northwest of the Acropolis in Athens, Greece. Its English name is the Late Latin composite form of the Greek name Areios Pagos, translated "Hill of Ares" (Ancient Greek: Ἄρειος Πάγος). Ares was supposed to have been tried by the gods on the Areopagus for the murder of Poseidon's son Halirrhothius (a typical example of an aetiological myth).
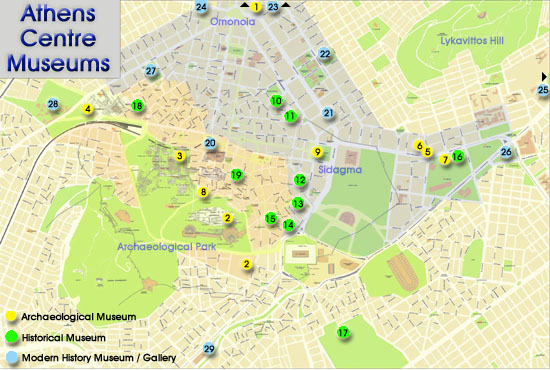
MUSEUMS
In the cultural heart of Athens